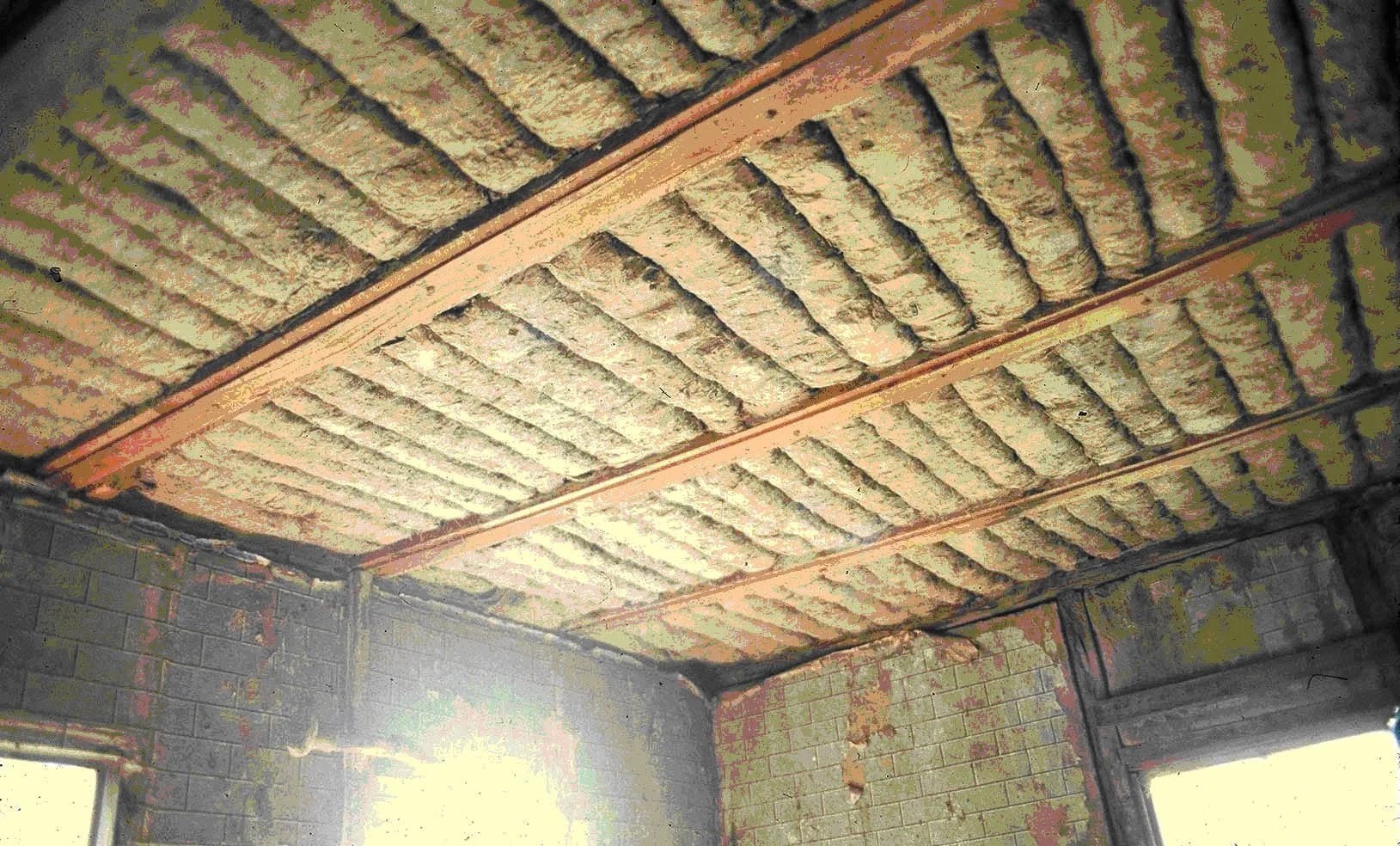
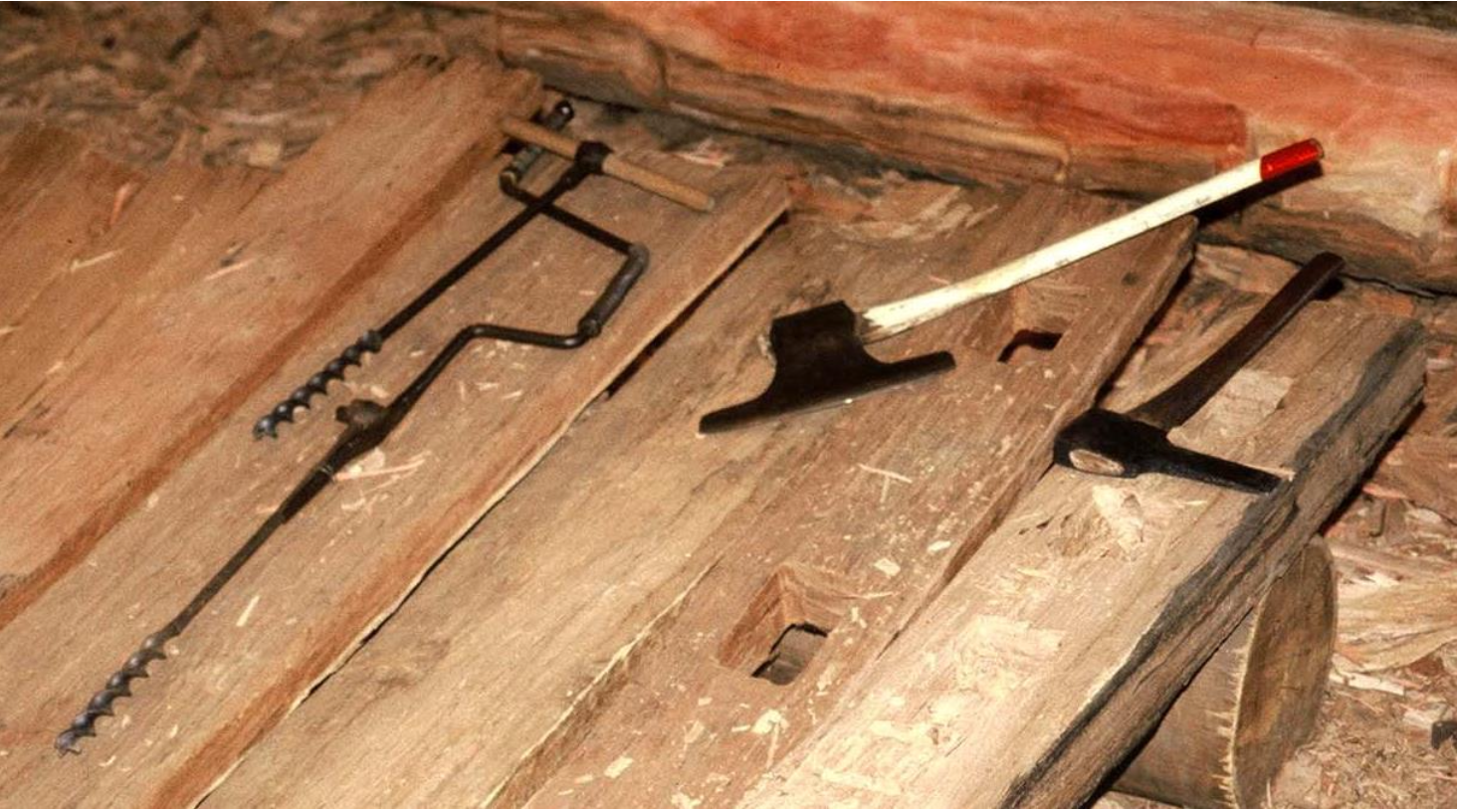
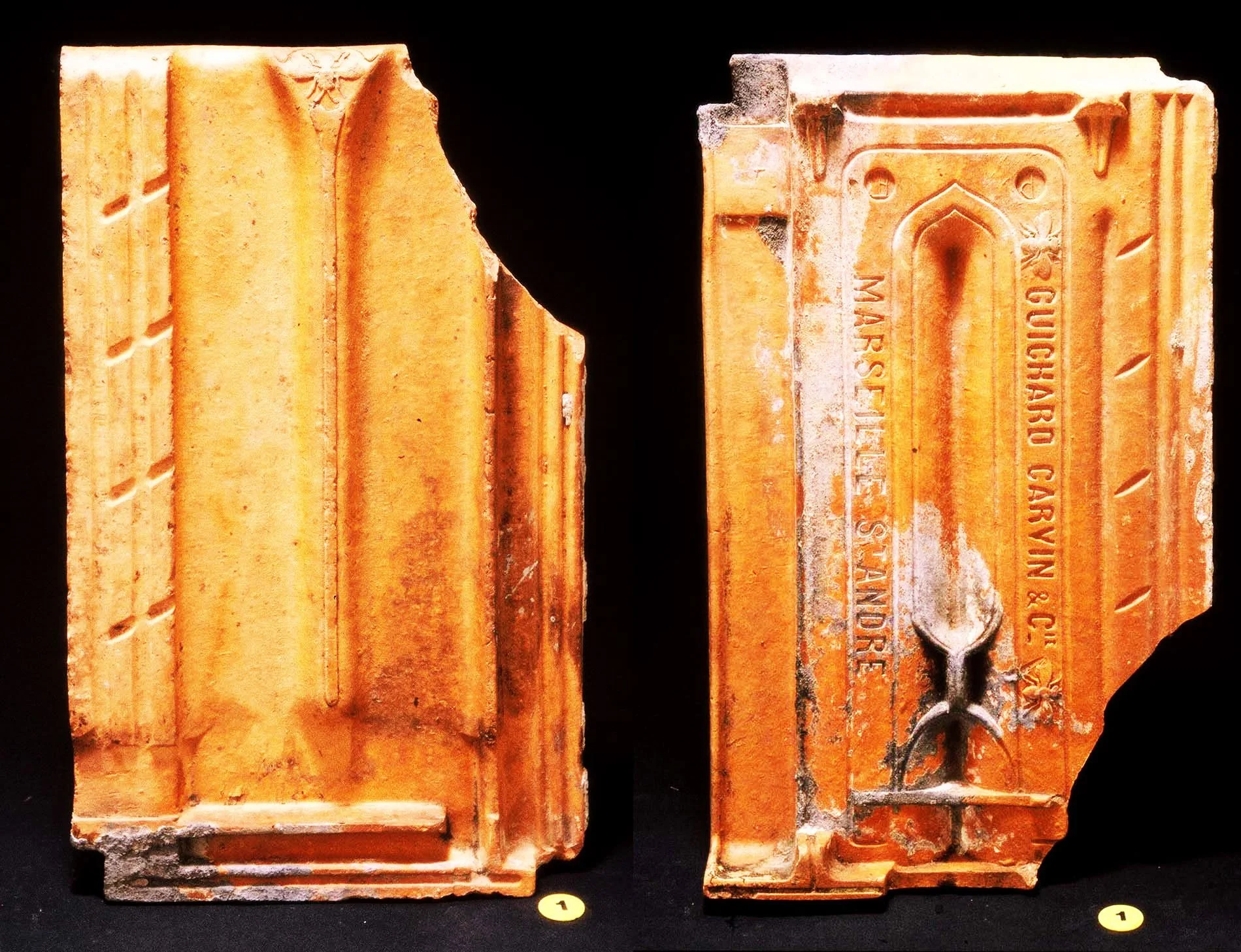
Australian Building: A Cultural Investigation
The construction of the Treasury Building, Melbourne, 1858. Photograph by Barnett Johnstone. State Library of Victoria H27165 [cropped].
This is a history of Australian building with an emphasis upon the development and spread of ideas and practices, and upon the tension between the European tradition and local conditions. It is a work in progress: some parts are fully developed, or have been published, whilst others are merely sketched in. Comments, contributions, and especially illustrations, will be gratefully received.
Send me an email at miles@mblewis.net.